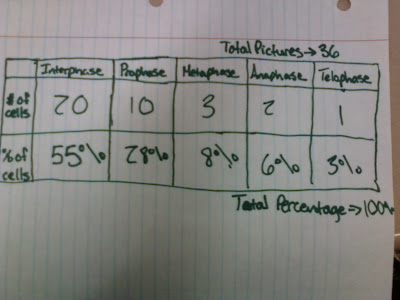
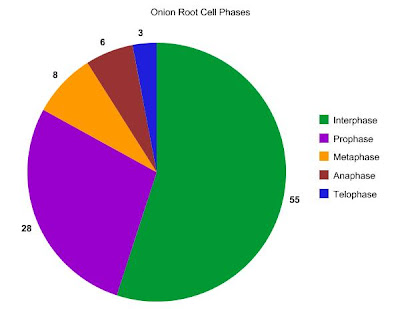
Questions about GATTACA!
Choose several of the following questions to discuss in a blog post reflection on the movie GATTACA. This reflection will become an artifact on your portfolio page 2 as part of your awareness of the effects of science upon society.
1. The following terms were used in the movie. How do they relate to the words we use: degenerate and invalid?
De-gene-erate
In-valid
Borrowed Ladder
2. Why do you think Vincent left his family, tearing his picture out of the family photo, after winning the swimming race against his brother?
He wanted to prove a point to his family that he wasn’t a loser.
3. Describe the relationship between Vincent and Anton.
Vincent didn’t like Anton because Anton was a perfect child and Vincent had alot of problems
4. When Jerome Morrow said to Vincent/Jerome, “They’re not looking for you. When they look at you, they only see me,” what did he mean? Can you find any parallels to this type of situation in real life? Because he is using Jermones DNA so people think of him as Jerome not Vincent.
When you are watching a movie you don’t think of the actor as himself but as the person who he is characterizing
5. Choose your favorite character from the film. Explain why you choose that person. Would you want to be that person? Why? Why not? I enjoyed the real Jerome Marrow because he was funny in some parts. I would not enjoy being him though because he wasn’t able to walk.
6. At the end of the film, you are told that the Doctor knew about Vincent all along. Why did the Doctor go along with the fraud? What would you have done if you were the Doctor?
The Doctor knew that it was Vincents dream. I would have let Vincent follow his dream.
7. The technology to do what was done in the movie is definitely possible within the next fifty years. Do you think that Vincent’s world could eventually happen in America? Why?
I believe that people will probably be desperate enough to go that far.
8. What do you think is wrong with the society portrayed in "GATTACA"? What is right?
People judging people because of ways there going to die is ridiculous.
9. What were the screenwriters trying to tell us through the episode of the 12-fingered pianist? Is anything wrong with engineering children to have 12 fingers if, as a result, they will be able to make extraordinarily beautiful music?
Its telling us that people who are different should be recognised.
10. You and your spouse are having a child and are at the Genetic Clinic pictured in the movie. What characteristics would you want for your child and what would you ask to be excluded? Why would you make those choices?
11. Picture yourself as either Vincent, Jerome, or Anton. Would you have acted the same or done things differently if you were in the same world as them?
12. How does the society in GATTACA resemble the type of society America was during the height of the eugenics movement?
1. The following terms were used in the movie. How do they relate to the words we use: degenerate and invalid?
De-gene-erate
In-valid
Borrowed Ladder
2. Why do you think Vincent left his family, tearing his picture out of the family photo, after winning the swimming race against his brother?
He wanted to prove a point to his family that he wasn’t a loser.
3. Describe the relationship between Vincent and Anton.
Vincent didn’t like Anton because Anton was a perfect child and Vincent had alot of problems
4. When Jerome Morrow said to Vincent/Jerome, “They’re not looking for you. When they look at you, they only see me,” what did he mean? Can you find any parallels to this type of situation in real life? Because he is using Jermones DNA so people think of him as Jerome not Vincent.
When you are watching a movie you don’t think of the actor as himself but as the person who he is characterizing
5. Choose your favorite character from the film. Explain why you choose that person. Would you want to be that person? Why? Why not? I enjoyed the real Jerome Marrow because he was funny in some parts. I would not enjoy being him though because he wasn’t able to walk.
6. At the end of the film, you are told that the Doctor knew about Vincent all along. Why did the Doctor go along with the fraud? What would you have done if you were the Doctor?
The Doctor knew that it was Vincents dream. I would have let Vincent follow his dream.
7. The technology to do what was done in the movie is definitely possible within the next fifty years. Do you think that Vincent’s world could eventually happen in America? Why?
I believe that people will probably be desperate enough to go that far.
8. What do you think is wrong with the society portrayed in "GATTACA"? What is right?
People judging people because of ways there going to die is ridiculous.
9. What were the screenwriters trying to tell us through the episode of the 12-fingered pianist? Is anything wrong with engineering children to have 12 fingers if, as a result, they will be able to make extraordinarily beautiful music?
Its telling us that people who are different should be recognised.
10. You and your spouse are having a child and are at the Genetic Clinic pictured in the movie. What characteristics would you want for your child and what would you ask to be excluded? Why would you make those choices?
11. Picture yourself as either Vincent, Jerome, or Anton. Would you have acted the same or done things differently if you were in the same world as them?
12. How does the society in GATTACA resemble the type of society America was during the height of the eugenics movement?